Kurşun zehirlenmesi
| Kurşun zehirlenmesi | |
|---|---|
| Diğer adlar | Plumbizm, colica pictorum, satürnizm, Devon kolik, ressam koliği |
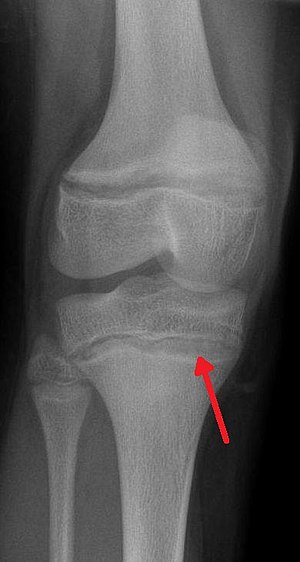 | |
| İnsanlarda kurşun zehirlenmesinin karakteristik bulgularını gösteren bir röntgen - yoğun metafiz çizgileri. | |
| Uzmanlık | Toksikoloji |
| Belirtiler | Zekâ geriliği, karın ağrısı, kabızlık, baş ağrısı, sinirlilik, hafıza sorunları, çocuk sahibi olamama, ellerde ve ayaklarda karıncalanma[1][2] |
| Komplikasyon | Kansızlık, epilepsi nöbeti, koma[1][2] |
| Nedenleri | Kirlenmiş hava, su, toz, gıda, tüketici ürünleri yoluyla kurşun maruziyeti [2] |
| Risk faktörü | Çocuk olmak[2] |
| Tanı | Kan kurşun seviyesi[2] |
| Ayırıcı tanı | Demir eksikliği anemisi, emilim bozukluğu, anksiyete bozukluğu, polinöropati[3] |
| Korunma | Kurşunu evden uzaklaştırmak, işyerinde gelişmiş izleme, ürünlerde kurşun yasaklayan yasalar[2][4][5][6] |
| Tedavi | Şelasyon tedavisi[4] |
| İlaç | Dimercaprol, sodyum kalsiyum edta, succimer[7] |
| Ölüm | 540,000 (2016)[2] |
Kurşun zehirlenmesi , vücuttaki kurşunun neden olduğu bir tür metal zehirlenmesidir.[2] Beyin en hassas olanıdır.[2] Belirtiler karın ağrısı, kabızlık, baş ağrısı, sinirlilik, hafıza sorunları, çocuk sahibi olamama ve ellerde ve ayaklarda karıncalanma olabilir.[1] Sebebi anlaşılamayan zekâ geriliğinin neredeyse %10’una neden olur ve davranış sorunları meydana gelebilir.[2] Bazı etkiler kalıcıdır.[2] Ağır vakalarda kansızlık, epilepsi nöbeti, koma veya ölüm meydana gelebilir.[1][2]
Kaynakça
- ^ a b c d "Lead Information for Workers". CDC. 30 Eylül 2013. 18 Ekim 2016 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 14 Ekim 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Kaynak hatası: Geçersiz
<ref>etiketi;WHO2016isimli refler için metin sağlanmadı (Bkz: Kaynak gösterme) - ^ Ferri, Fred F. (2010). Ferri's differential diagnosis : a practical guide to the differential diagnosis of symptoms, signs, and clinical disorders (2nd bas.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Mosby. s. Chapter L. ISBN 978-0323076999.
- ^ a b Kaynak hatası: Geçersiz
<ref>etiketi;Dap2014isimli refler için metin sağlanmadı (Bkz: Kaynak gösterme) - ^ Kaynak hatası: Geçersiz
<ref>etiketi;Need2004isimli refler için metin sağlanmadı (Bkz: Kaynak gösterme) - ^ Kaynak hatası: Geçersiz
<ref>etiketi;CDC2016Previsimli refler için metin sağlanmadı (Bkz: Kaynak gösterme) - ^ Kaynak hatası: Geçersiz
<ref>etiketi;Gra2007isimli refler için metin sağlanmadı (Bkz: Kaynak gösterme)
Kaynak hatası: <references> üzerinde tanımlanan "Pearson03" adındaki <ref> etiketi önceki metinde kullanılmıyor. (Bkz: Kaynak gösterme)
Kaynak hatası: <references> üzerinde tanımlanan "Pearson03-370" adındaki <ref> etiketi önceki metinde kullanılmıyor. (Bkz: Kaynak gösterme)
<references> üzerinde tanımlanan "leadout" adındaki <ref> etiketi önceki metinde kullanılmıyor. (Bkz: Kaynak gösterme)Kaynakçalar
- Brunton, L.L.; Goodman, L.S.; Blumenthal, D.; Buxton, I.; Parker, K.L., (Ed.) (2007). "Principles of toxicology". Goodman and Gilman's Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics. McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-144343-2.
- Casarett, LJ; Klaassen, CD; Doull, J, (Ed.) (2007). "Toxic effects of metals". Casarett and Doull's Toxicology: The Basic Science of Poisons (7th bas.). McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-147051-3.
- Chisolm, J.J. (2004). "Lead poisoning". Crocetti, M.; Barone, M.A.; Oski, F.A. (Ed.). Oski's Essential Pediatrics (2nd bas.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-3770-8. Geçersiz
|chapter-url-access=registration(yardım) - Dart, R.C.; Hurlbut, K.M.; Boyer-Hassen, L.V. (2004). "Lead". Dart, RC (Ed.). Medical Toxicology (3rd bas.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-2845-4.
- Grant, L.D. (2009). "Lead and compounds". Lippmann, M. (Ed.). Environmental Toxicants: Human Exposures and Their Health Effects (3rd bas.). Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 978-0-471-79335-9.
- Henretig F.M. (2006). "Lead". Goldfrank, LR (Ed.). Goldfrank's Toxicologic Emergencies (8th bas.). McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-143763-9.
- Hodge, A. Trevor (1992). Roman Aqueducts & Water Supply. Londra: Duckworth. ISBN 978-0-7156-2194-3.
- Kosnett M.J. (2005). "Lead". Brent, J (Ed.). Critical Care Toxicology: Diagnosis and Management of the Critically Poisoned Patient. Gulf Professional Publishing. ISBN 978-0-8151-4387-1.
- Kosnett, M.J. (2007). "Heavy metal intoxication and chelators". Katzung, B.G. (Ed.). Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-145153-6.
- Kosnett, M.J. (18 Eylül 2006). "Lead". Olson, K.R. (Ed.). Poisoning and Drug Overdose (5th bas.). McGraw-Hill Professional. s. 2006. ISBN 978-0-07-144333-3.
- Menkes, J.H. (2006). "Toxic and nutritional disorders". Menkes, J.H.; Sarnat, H.B.; Maria, B.L. (Ed.). Child Neurology (7th bas.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. s. 706. ISBN 978-0-7817-5104-9.
- Merrill, J.C.; Morton, J.J.P.; Soileau, S.D. (2007). "Metals". Hayes, A.W. (Ed.). Principles and Methods of Toxicology (5th bas.). CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8493-3778-9.
- Mycyk, M.; Hryhorczuk, D.; Amitai, Y. (2005). "Lead". Erickson, TB; Ahrens, WR; Aks, S; Ling, L (Ed.). Pediatric Toxicology: Diagnosis and Management of the Poisoned Child. McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-141736-5.
- Olson, K.R. (2007). "Poisoning". McPhee, S.J.; Tierney, L.M.; Papadakis, M.A. (Ed.). Current Medical Diagnosis and Treatment (46th bas.). McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-147247-0. Geçersiz
|chapter-url-access=registration(yardım) - Pearson H.A.; Schonfeld, D.J. (2003). "Lead". Rudolph, C.D. (Ed.). Rudolph's Pediatrics (21st bas.). McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-8385-8285-5.
- Rambousek, A.J., (Ed.) (2008). "The symptoms and treatment of industrial poisoning". Industrial Poisoning from Fumes, Gases, and Poisons of Manufacturing Processes. READ BOOKS. ISBN 978-1-4086-7025-5.
- Rubin, R.; Strayer, D.S., (Ed.) (2008). "Environmental and nutritional pathology". Rubin's Pathology: Clinicopathologic Foundations of Medicine (5th bas.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-9516-6.
- Salvato, J.A.; Nemerow, N.L.; Agardy, F.J., (Ed.) (2003). "Noninfectious and noncommunicable diseases and conditions associated with the environment, including air, water, and food". Environmental Engineering (5th bas.). John Wiley and Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-41813-9.
- Trevor, A.J.; Katzung, B.G.; Masters, S.B., (Ed.) (2007). "Heavy metals". Katzung & Trevor's Pharmacology: Examination & Board Review (8th bas.). McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-148869-3.
- Yu, M.H. (2005). "Soil and water pollution: Environmental metals and metalloids". Environmental Toxicology: Biological and Health Effects of Pollutants. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-56670-670-4.
Dış bağlantılar
- Binns, H.J.; Ricks, O.B. "Helping Parents Prevent Lead Poisoning". ERIC Digest. 5 Mayıs 2004 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 2 Ağustos 2020.
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (20 Ağustos 2007). "Lead Toxicity". Environmental Health and Medicine Education. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Course: WB 1105. 2 Ekim 2015 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 2 Ağustos 2020.
- Health and Safety Executive UK. "Lead". Working safely with lead. HSE. 6 Kasım 2009 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 2 Ağustos 2020.
- Karalus, Daniel E (2010). "Review: The Great Lead Water Pipe Disaster". Electronic Green Journal. 1 (29). 27 Nisan 2018 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 2 Ağustos 2020.
- Katz, N.L. (26 Haziran 2007). "City payout to Brooklyn family largest ever in lead poisoning". NY Daily News. 3 Haziran 2011 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 2 Ağustos 2020.
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (20 Haziran 2018). "Lead". NIOSH Workplace Safety & Health Topics. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 4 Nisan 2004 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 2 Ağustos 2020.
- National Pollutant Inventory. "Lead and compounds: Health effects". Fact Sheets. Canberra, Australia: Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population and Communities. 20 Mart 2012 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 2 Ağustos 2020.
- National Safety Council (2008). "Lead Poisoning" (PDF). Fact Sheets. Itasca, Illinois, U.S.: National Safety Council. 22 Aralık 2017 tarihinde kaynağından (PDF) arşivlendi. Erişim tarihi: 11 Haziran 2016.
- Küpper, Hendrik (2017). "Chapter 15. Lead Toxicity in Plants". Astrid, S.; Helmut, S.; Sigel, R. K. O. (Ed.). Lead: Its Effects on Environment and Health. Metal Ions in Life Sciences. 17. de Gruyter. ss. 491-500. doi:10.1515/9783110434330-015. ISBN 9783110434330. PMID 28731308.
