Hash tablosu: Revizyonlar arasındaki fark
| [kontrol edilmiş revizyon] | [kontrol edilmiş revizyon] |
k düzen |
Superyetkin (mesaj | katkılar) Kaynak gösterme hatası giderildi |
||
| 16. satır: | 16. satır: | ||
| sayfalar = 513–558 |
| sayfalar = 513–558 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
</ref><ref name="cormen" |
</ref><ref name="cormen">{{cite book |
||
| authorlink = Thomas H. Cormen |
|||
| first = Thomas H. |
|||
| last = Cormen |
|||
| coauthors = [[Charles E. Leiserson|Leiserson, Charles E.]]; [[Ronald L. Rivest|Rivest, Ronald L.]]; [[Clifford Stein|Stein, Clifford]] |
|||
| title = [[Introduction to Algorithms]] |
|||
| publisher = MIT Press and McGraw-Hill |
|||
| year= 2001 |
|||
| isbn = 978-0-262-53196-2 |
|||
| edition = 2 |
|||
| pages=221–252 |
|||
| nopp = Chapter 11: Hash Tables |
|||
}}</ref> |
|||
Birçok durumda komut tablolarının [[arama ağaçları]] veya herhangi bir [[Çizelge (bilişim)|çizelge]] başvuru yapısından daha verimli olduğu ortaya çıkar. Bu sebeple birçok [[yazılım]] çeşidinde, özellikle [[birleşmeli dizin]]lerde, [[veritabanı indisi|veritabanı indislemesi]]nde, [[önbellek]]lerde ve [[küme veri yapısı|kümelerde]] kullanılır. |
Birçok durumda komut tablolarının [[arama ağaçları]] veya herhangi bir [[Çizelge (bilişim)|çizelge]] başvuru yapısından daha verimli olduğu ortaya çıkar. Bu sebeple birçok [[yazılım]] çeşidinde, özellikle [[birleşmeli dizin]]lerde, [[veritabanı indisi|veritabanı indislemesi]]nde, [[önbellek]]lerde ve [[küme veri yapısı|kümelerde]] kullanılır. |
||
| 44. satır: | 56. satır: | ||
Cryptographic hash functions are believed to provide good hash functions for any table size ''s'', either by modulo reduction or by bit masking. They may also be appropriate, if there is a risk of malicious users trying to [[denial of service attack|sabotage]] a network service by submitting requests designed to generate a large number of collisions in the server's hash tables.{{Citation needed|date=February 2007}}<!-- see discussion on talk page; just needs a reference --> <!-- However, these presumed qualities are hardly worth their much larger computational cost and algorithmic complexity, and the risk of sabotage can be avoided by cheaper methods (such as applying a secret [[salt (cryptography)|salt]] to the data, or using a [[universal hash function]]). --> |
Cryptographic hash functions are believed to provide good hash functions for any table size ''s'', either by modulo reduction or by bit masking. They may also be appropriate, if there is a risk of malicious users trying to [[denial of service attack|sabotage]] a network service by submitting requests designed to generate a large number of collisions in the server's hash tables.{{Citation needed|date=February 2007}}<!-- see discussion on talk page; just needs a reference --> <!-- However, these presumed qualities are hardly worth their much larger computational cost and algorithmic complexity, and the risk of sabotage can be avoided by cheaper methods (such as applying a secret [[salt (cryptography)|salt]] to the data, or using a [[universal hash function]]). --> |
||
<!--Some authors claim that good hash functions should have the [[avalanche effect]]; that is, a single-bit change in the input key should affect, on average, half the bits in the output. Some popular hash functions do not have this property.<ref name="mulvey1">Bret Mulvey, [http://bretm.home.comcast.net/~bretm/hash/ Hash Functions]. Accessed April 11, 2009</ref> --> |
<!--Some authors claim that good hash functions should have the [[avalanche effect]]; that is, a single-bit change in the input key should affect, on average, half the bits in the output. Some popular hash functions do not have this property.<ref name="mulvey1">Bret Mulvey, [http://bretm.home.comcast.net/~bretm/hash/ Hash Functions]. Accessed April 11, 2009</ref> --> |
||
<!-- === Perfect hash function === |
<!-- === Perfect hash function === |
||
If all keys are known ahead of time, a [[perfect hash function]] can be used to create a perfect hash table that has no collisions. If [[minimal perfect hashing]] is used, every location in the hash table can be used as well. |
If all keys are known ahead of time, a [[perfect hash function]] can be used to create a perfect hash table that has no collisions. If [[minimal perfect hashing]] is used, every location in the hash table can be used as well. |
||
Perfect hashing allows for constant time lookups in the worst case. This is in contrast to most chaining and open addressing methods, where the time for lookup is low on average, but may be very large (proportional to the number of entries) for some sets of keys. --> |
Perfect hashing allows for constant time lookups in the worst case. This is in contrast to most chaining and open addressing methods, where the time for lookup is low on average, but may be very large (proportional to the number of entries) for some sets of keys. --> |
||
== Kaynakça == |
== Kaynakça == |
||
{{kaynakça}} |
{{kaynakça}} |
||
Sayfanın 17.06, 23 Nisan 2014 tarihindeki hâli
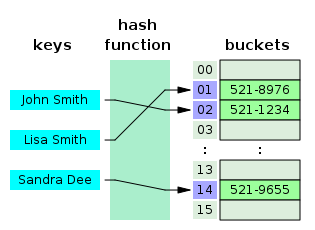
Bilişim bilimlerinde komut çizelgesi (İng. hash table veya hash map - hash = doğramak), komut işlevini tanıyıcı değer olarak bilinen benzersiz anahtarı bir değerle (mesela kişi adını telefon numarasıyla) eşleyen bir veri yapısıdır. Böylece komut çizelgesi bir birleşik dizidir. Komut işlevi, ilişkin değerin arandığı anahtarı bir dizi elemanının indisine ("dilim" veya "kova") çevirerir (doğramaya bezediğinden "hash" denmiştir). İdealde komut işlevinin mümkün olan her anahtarı farklı benzersiz dilim indisine eşlemesi, gerçekte (komut anahtarları sâbit, yani tabloya oluşumundan sonra yeni öge eklenmemesi durumu dışında) enderdir. Çoğu komut çizelgesi tasarımları "çarpışmaları", yani farklı anahtarlara aynı komut değerinin bulunması durumunu normal olarak görerek bir şekilde uzlaştırır. Uygun boyutlandırılmış bir komut çizelgesinda her bakış için ortalama mâliyet (gerekli komut sayısı), çizelgede depolanmış eleman sayısından bağımsızdır. Ayrıca birçok komut çizelge tasarımları, anahtar-değer çiftlerinin keyfî araya sokuluş ve çıkarışlarına (aslında sönümlenmiş[1])sabit işlem başı maliyetle izin verir.[2][3]
Birçok durumda komut tablolarının arama ağaçları veya herhangi bir çizelge başvuru yapısından daha verimli olduğu ortaya çıkar. Bu sebeple birçok yazılım çeşidinde, özellikle birleşmeli dizinlerde, veritabanı indislemesinde, önbelleklerde ve kümelerde kullanılır.
Komut çizelgelerini kriptografi ve veri iletiminde kullanılan komut listeleri ve komut ağaçlarıyla karıştırmamalıdır.
Komut işlevi
Komut çizelgesi algoritmasının temelinde basit bir dizin ögesidir. Bu ögeye kısaca komut çizelgesi (İng. hash table). Komut çizelgesi algoritmaları, veri ögelerinin kiplemelerinden bir indeks hesaplayıp bunu veriyi bir dizine yerleştirmeye kullanılır. Bu hesabın uygulaması komut işlevidir ve f:
indeks = f(kipleme, dizinUzunlugu)
Komut işlevi, veri kiplemesi dizininden oluşturulan indeksi hesaplar. dizinUzunlugu, dizinin büyüklüğüdür.
Birleştirici dil veya başka alçak düzeyli dillerde çoğu zaman sıradan bir komut işleviyle bir veya iki satıriçi makina komutu içeren bir indeks oluşturulur.
Kaynakça
- ^ Charles E. Leiserson, Amortized Algorithms, Table Doubling, Potential Method Lecture 13, course MIT 6.046J/18.410J Introduction to Algorithms - Fall 2005
- ^
Donald Knuth (1998). The Art of Computer Programming'. 3: Sorting and Searching (2nd bas.). ss. 513–558. ISBN 0-201-89685-0. Bilinmeyen parametre
|not=görmezden gelindi (yardım); Bilinmeyen parametre|yayımevi=görmezden gelindi (yardım) - ^ Cormen, Thomas H. (2001). Introduction to Algorithms (2 bas.). MIT Press and McGraw-Hill. ss. 221–252. ISBN 978-0-262-53196-2. Bilinmeyen parametre
|coauthors=görmezden gelindi (yardım); Geçersiz|ssyok=Chapter 11: Hash Tables(yardım)
