Beta Pegasi
Beta Pegasi'nin Kanatlıat takımyıldızındaki konumu | |
| Gözlem verisi Dönem J2000 Ekinoks J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Takımyıldız | Kanatlıat |
| Sağ açıklık (α) | 23sa 03d 46.45746s[1] |
| Dik açıklık (δ) | +28° 04′ 58.0336″[1] |
| Görünür büyüklük (V) | 2.42[2] (2.31 - 2.74)[3] |
| Sınıflandırma | |
| Tayfsal sınıf | M2.5II–IIIe[4] |
| U−B renk ölçeği | +1.96[2] |
| B−V renk ölçeği | +1.67[2] |
| Değişen yıldız tipi | Yarı düzenli[5] |
| Astrometri | |
| Dikey hız () | +8.7[6] km/s |
| Özdevinim (μ) | RA: +187.65[1] mys/y Dec.: +136.93[1] mys/y |
| Iraklık açısı (π) | 16.64 ± 0.15[1] mys |
| Uzaklık | 196 ± 2 Iy (60.1 ± 0.5 pc) |
| Mutlak büyüklük (V) | −1.41[7] |
| Özellikler | |
| Kütle (m) | 2.1[8] M☉ |
| Yarıçap (r) | 95 R☉ |
| Yüzey kütle çekimi (log g) | 1.20[9] cgs |
| Sıcaklık | 3,689[9] K |
| Metallik [Fe/H] | –0.11[9] |
| Dönüş hızı () | 9.7[10] km/s |
| Katalog belirtmeleri | |
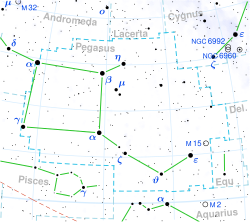
Beta Pegasi (β Pegasi, Beta Peg, β Peg) veya Scheat, Kanatlıat takımyıldızında bulunan bir yıldızdır. Dünyadan 196 ışık yılı uzaklıkta yer almakta olup Kanatlıat takımyıldızındaki ikinci en parlak yıldızdır. Dikdörtgen bir yıldız işareti olan Kanatlı Büyük Karesi'nin sağ üst köşesini oluşturur.
Kaynakça[değiştir | kaynağı değiştir]
- ^ a b c d e van Leeuwen, F. (Kasım 2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2). ss. 653-664. arXiv:0708.1752 $2. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357.
- ^ a b c Johnson, H. L.; Iriarte, B.; Mitchell, R. I.; Wisniewskj, W. Z. (1966). "UBVRIJKL photometry of the bright stars". Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory. 4 (99). s. 99. Bibcode:1966CoLPL...4...99J.
- ^ "Query= bet Peg", General Catalogue of Variable Stars, Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg, 15 Aralık 2018 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi, erişim tarihi: 6 Ocak 2020
- ^ a b "V* bet Peg -- Pulsating variable Star", SIMBAD, Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg, 26 Mart 2016 tarihinde kaynağından arşivlendi, erişim tarihi: 6 Ocak 2020
- ^ Tabur, V.; Bedding, T. R.; Kiss, L. L.; Moon, T. T.; Szeidl, B.; Kjeldsen, H. (Aralık 2009), "Long-term photometry and periods for 261 nearby pulsating M giants", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 400 (4), ss. 1945-1961, arXiv:0908.3228 $2, Bibcode:2009MNRAS.400.1945T, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2009.15588.x
- ^ Wilson, Ralph Elmer (1953), "General Catalogue of Stellar Radial Velocities", Washington, Washington: Carnegie Institution of Washington, Bibcode:1953GCRV..C......0W
- ^ Huang, W.; Wallerstein, G.; Stone, M. (2012), "A catalogue of Paschen-line profiles in standard stars", Astronomy & Astrophysics, cilt 547, ss. A62, arXiv:1210.7893 $2, Bibcode:2012A&A...547A..62H, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201219804.
- ^ Tsuji, Takashi (Mayıs 2007). "Isotopic abundances of Carbon and Oxygen in Oxygen-rich giant stars". Kupka, F.; Roxburgh, I.; Chan, K. (Ed.). Convection in Astrophysics, Proceedings of IAU Symposium #239 held 21-25 August, 2006 in Prague, Czech Republic. Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union. 2. ss. 307-310. arXiv:astro-ph/0610180 $2. Bibcode:2007IAUS..239..307T. doi:10.1017/S1743921307000622.
- ^ a b c Soubiran, C.; Bienaymé, O.; Mishenina, T. V.; Kovtyukh, V. V. (2008), "Vertical distribution of Galactic disk stars. IV. AMR and AVR from clump giants", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 480 (1), ss. 91-101, arXiv:0712.1370 $2, Bibcode:2008A&A...480...91S, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078788
- ^ Massarotti, Alessandro; Latham, David W.; Stefanik, Robert P.; Fogel, Jeffrey (Ocak 2008), "Rotational and Radial Velocities for a Sample of 761 HIPPARCOS Giants and the Role of Binarity", The Astronomical Journal, 135 (1), ss. 209-231, Bibcode:2008AJ....135..209M, doi:10.1088/0004-6256/135/1/209
| Astronomi ile ilgili bu madde taslak seviyesindedir. Madde içeriğini genişleterek Vikipedi'ye katkı sağlayabilirsiniz. |