SHA-2: Revizyonlar arasındaki fark
| [kontrol edilmemiş revizyon] | [kontrol edilmemiş revizyon] |
kDeğişiklik özeti yok |
translation from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SHA-2 Etiketler: tanım değiştirme Görsel Düzenleyici |
||
| 1. satır: | 1. satır: | ||
SHA-2, Amerika Birleşik Devletleri Ulusal Güvenlik Ajansı tarafından dizayn edilmiş kriptografik Hash fonksiyonları kümesidir. <ref>[http://www.staff.science.uu.nl/~werkh108/docs/study/Y5_07_08/infocry/project/Cryp08.pdf "On the Secure Hash Algorithm family"] (PDF).</ref> Kriptografik Hash fonksiyonları, hesaplanmış “hash” (çalıştırılan algoritmanın çıktısı) ile bilinen ve beklenen hash değerinin karşılaştırılmasıyla, dijital veri üzerinde yürüyen matematiksel operasyonlardır. Herhangi bir kişi verinin bütünlüğüne karar verebilir. Örneğin, yüklenmiş bir dosyanın hash ’ini hesaplamak ve sonucu önceden açıklanmış hash sonucu ile karşılaştırmak, yüklemenin değiştirilip değiştirilmediğini veya üzerinde oynama yapılıp yapılmadığını gösterebilir. <ref>[https://www.lifewire.com/cryptographic-hash-function-2625832 "Cryptographic Hash Function"]. About.com</ref> Kriptografik Hash fonksiyonlarının kilit noktası çakışma dirençleridir: hiç kimse aynı hash çıktısı veren iki farklı girdi bulamamalı. |
|||
'''SHA-2''', ABD [[Ulusal Güvenlik Ajansı]] (NSA) tarafından dizayn edilen bir kriptografik özet fonksiyonudur. |
|||
SHA-2, kendinden önce gelen SHA-1’den önemli farklılıklar içermektedir. SHA-2 ailesi basamakları (hash değerleri) 224, 256, 384 veya 512 bit olan altı hash fonksiyonundan oluşur: SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512, SHA-512/224, SHA-512/256.SHA-256 ve SHA-512 sırasıyla 32-bit ve 64-bitlik kelimelerle hesaplanmış orijinal hash fonksiyonlarıdır. Farklı kaydırma miktarları ve toplama sabitleri kullanırlar ancak yapıları neredeyse aynıdır sadece yuvarlama sayısında farklıdırlar. SHA-224 ve SHA-384 ilk ikisinin farklı başlangıç değerleri ile hesaplanmış, basitçe kesilmiş versiyonlarıdır. SHA-512/224 ve SHA-512/256 da SHA-512’nin kesilmiş versiyonlarıdır ama başlangıç değerleri Federal Bilgi İşleme Standardı (FIPS) PUB 180-4’te tanımlanmış metot kullanılarak üretilmiştir. SHA-2, Ulusal Standartlar ve Teknoloji Enstitüsü (NIST) bir Birleşik Devletler federal standardı (FIPS) tarafından 2001’de yayınlanmıştır. SHA-2 algoritmalar ailesi Birleşik Devletler 6829355 patentinde patentlenmiştir.<ref>[https://worldwide.espacenet.com/textdoc?DB=EPODOC&IDX=US6829355 US 6829355]</ref> Birleşik Devletler patenti telifsiz lisans altında yayımlamıştır.<ref>[https://datatracker.ietf.org/ipr/858/ "Licensing Declaration for US patent 6829355.".]</ref> |
|||
SHA-2'nin SHA'nın önceki versiyonlarından en büyük farkı farklı uzunluklarda çıktı verebilen ve farklı blok uzunluğu kullanan türlerinin bulunması. SHA ve [[SHA-1]]'de çıktı uzunluğunu metni 512 bitlik bloklara bölerek yapılan işlemler sonucu elde ediyordu. SHA-2'de ise metin 1024 ve 512 bitlik bloklara bölünebilerek, 224, 256, 384 ve 512 bitlik çıktı alınabiliyordu. |
|||
2005’te, SHA-1 çakışmalarını önceden mümkün olduğu düşünülenden 2000 daha az adımda bulmak için bir algoritma geliştirilmiştir. <ref> [https://www.schneier.com/blog/archives/2005/02/cryptanalysis_o.html "Schneier on Security: Cryptanalysis of SHA-1"]. Schneier.com.</ref> 2017’de SHA-1 çakışmasının bir örneği yayımlanmıştır.<ref>Cryptology Group at Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica (CWI) and the Google Research Security, Privacy and Anti-abuse Group. [https://shattered.io/ "Shattered: We have broken SHA-1 in practice"]. SHAttered.</ref> SHA-1 tarafından bırakılan güvenlik marjini planlanandan zayıftır ve bu sebeple, kullanımı artık dijital imzalar gibi çakışma direncine bağımlı uygulamalar için önerilmemektedir. SHA-2, SHA-1 algoritmasına bazı benzerlikler taşısa da, bu ataklar SHA-2’ye başarılı bir şekilde genişletilememiştir. |
|||
Şu anda en iyi açık ataklar, aşağıda Kriptanaliz ve Doğrulama bölümünde gösterildiği gibi SHA-256’nın 52 yuvarlaması veya SHA-512’nin 57 yuvarlaması için öngörüntü direncini ve SHA-256’nin 46 yuvarlaması için çakışma direncini kırmaktadır. <ref> Dmitry Khovratovich, Christian Rechberger & Alexandra Savelieva (2011). [http://eprint.iacr.org/2011/286.pdf "Bicliques for Preimages: Attacks on Skein-512 and the SHA-2 family"] (PDF). IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive. 2011:286.</ref><ref>Mario Lamberger & Florian Mendel (2011). [http://eprint.iacr.org/2011/037.pdf "Higher-Order Differential Attack on Reduced SHA-256"] (PDF). IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive. 2011:37.</ref> |
|||
== Hash Standartları == |
|||
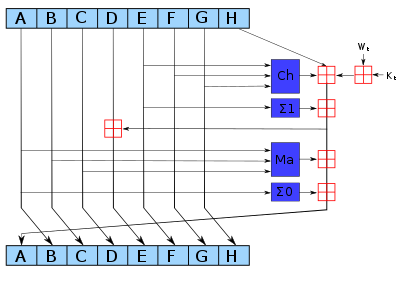
[[File:SHA-2.svg|bağlantı=https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:SHA-2.svg|sağ|küçükresim|400x400pik|One iteration in a SHA-2 family compression function. The blue components perform the following operations: |
|||
<math>\operatorname{Ch}(E,F,G) = (E \and F) \oplus (\neg E \and G)</math> |
|||
<math>\operatorname{Ma}(A,B,C) = (A \and B) \oplus (A \and C) \oplus (B \and C)</math> <math>\Sigma_0(A) = (A\!\ggg\!2) \oplus (A\!\ggg\!13) \oplus (A\!\ggg\!22)</math> <math>\Sigma_1(E) = (E\!\ggg\!6) \oplus (E\!\ggg\!11) \oplus (E\!\ggg\!25)</math> |
|||
The bitwise rotation uses different constants for SHA-512. The given numbers are for SHA-256. |
|||
The red <math>\color{red}\boxplus</math> is addition modulo 2<sup>32</sup> for SHA-256, or 2<sup>64</sup> for SHA-512.]] |
|||
FIPS PUB 180-2’nin yayımlanmasıyla, NIST SHA ailesinde üç tane ek hash fonksiyonu eklemiştir. Algoritmalar toplu olarak SHA-2 diye bilinir ve basamak uzunlukları (bit cinsinden) ile isimlendirilmişlerdir: SHA-256, SHA-384, ve SHA-512. |
|||
Algoritmalar ilk olarak 2001’de FIPS PUB 180-2 taslağında, public review and comments (kamu değerlendirmesi ve yorumları???) kabul edildiğinde, yayımlanmışlardır. Ağustos 2002’de FIPS PUB 180-2, Nisan 1995’te yayımlanan FIPS PUB 180-1’in yerini alarak yeni Güvenli Hash Standardı haline geldi. Güncellenmiş standart, SHA-2 ailesinin iç çalışmalarını tanımlamasıyla tutarlı güncellenmiş teknik notasyonla birlikte orijinal SHA-1 algoritmasını içerir. <ref>Federal Register Notice 02-21599, [https://federalregister.gov/a/02-21599 Announcing Approval of FIPS Publication 180-2]</ref> |
|||
Şubat 2004’te FIPS PUB 180-2 için, iki anahtarlı Üçlü DES’in anahtar uzunluğuyla eşleşmesi amacıyla tanımlanmış ek bir değişkeni,SHA-224, belirten bir değişiklik bildirimi yayımlandı. <ref>[http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/fips/fips180-2/fips180-2withchangenotice.pdf "FIPS 180-2 with Change Notice 1"] (PDF). csrc.nist.gov</ref> Ekim 2008’de standart, FIPS PUB 180-3’te değişiklik bildirimindeki SHA-224 dahil güncellendi, ama bunun dışında standartta başka temel değişim yapılmadı. Standardı güncellemekteki başlıca motivasyon hash algoritmaları ve kullanım önerileri hakkındaki güvenlik bilgisini Special Publications 800-107 ve 800-57’ye yeniden yerleştirmekti.<ref>Federal Register Notice E8-24743, [https://federalregister.gov/a/E8-24743 Announcing Approval of FIPS Publication 180-3]</ref> <ref name=":0">FIPS SP 800-107 [http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/nistpubs/800-107-rev1/sp800-107-rev1.pdf Recommendation for Applications Using Approved Hash Algorithms]</ref><ref name=":1">FIPS SP 800-57 [http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/nistpubs/800-57/sp800-57_part1_rev3_general.pdf Recommendation for Key Management: Part 1: General]</ref>Detaylı test verisi ve örnek mesaj özetleri de standarttan kaldırıldı ve ayrı belge olarak temin edildi.<ref>[http://csrc.nist.gov/groups/ST/toolkit/examples.html#aHashing "NIST.gov - Computer Security Division - Computer Security Resource Center"]</ref> |
|||
In January 2011, NIST published SP800-131A, which specified a move from the current minimum security of 80-bits (provided by SHA-1) allowable for federal government use until the end of 2013, with 112-bit security (provided by SHA-2) being the minimum requirement current thereafter, and the recommended security level from the publication date. <ref>FIPS SP 800-131A [http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/nistpubs/800-131A/sp800-131A.pdf Recommendation for Transitioning the Use of Cryptographic Algorithms and Key Lengths]</ref> |
|||
Mart 2012’de standart, SHA-512/224 ve SHA-512/256 hash fonksiyonları eklenerek ve SHA-512’nin kesilmiş versiyonları için başlangıç değerleri üretmek üzere bir metot tanımlanarak FIPS PUB 180-4’te güncellendi. Buna ek olarak, gerçek-zamanlı video veya ses beslemesi gibi hash verisinin içerik üretimi ile aynı anda hesaplanmasına izin verilerek, girdi verisini hash hesaplamasından önce eklemedeki kısıtlama kaldırıldı. Son veri bloğunu eklemek hala hash çıktısından önce gerçekleştirilmelidir. <ref>Federal Register Notice 2012-5400, [https://federalregister.gov/a/2012-5400 Announcing Approval of FIPS Publication 180-4]</ref> |
|||
Temmuz 2012’de NIST, kriptografik anahtar yönetimi için rehberlik sağlayan SP800-57’yi tekrar gözden geçirdi. Yayın, 2013’ten sonra hash güvenliği 112-bitten az olan dijital imzaların üretilmesine izin vermemektedir. 2007’de olan önceki gözden geçirme kesmenin 2010’un sonu olacağını belirtmişti??????.<ref name=":1" /> Ağustos 2012’de NIST, SP800-107’yi aynı şekilse gözden geçirdi.<ref name=":0" /> |
|||
NIST hash fonksiyonu yarışması yeni hash fonksiyonu SHA-3’ü 2012 yılında seçti.<ref> [https://www.nist.gov/news-events/news/2012/10/nist-selects-winner-secure-hash-algorithm-sha-3-competition "NIST Selects Winner of Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA-3) Competition"]</ref> SHA-3 algoritması, SHA-2’den türetilmemiştir. |
|||
== Uygulamalar == |
|||
== Kriptanaliz ve Doğrulama == |
|||
=== Resmi Doğrulama === |
|||
== Test Değerleri == |
|||
Hash values of an empty string (i.e., a zero-length input text). |
|||
{{color|green|SHA224("")}} |
|||
0x d14a028c2a3a2bc9476102bb288234c415a2b01f828ea62ac5b3e42f |
|||
{{color|green|SHA256("")}} |
|||
0x e3b0c44298fc1c149afbf4c8996fb92427ae41e4649b934ca495991b7852b855 |
|||
{{color|green|SHA384("")}} |
|||
0x 38b060a751ac96384cd9327eb1b1e36a21fdb71114be07434c0cc7bf63f6e1da274edebfe76f65fbd51ad2f14898b95b |
|||
{{color|green|SHA512("")}} |
|||
0x cf83e1357eefb8bdf1542850d66d8007d620e4050b5715dc83f4a921d36ce9ce47d0d13c5d85f2b0ff8318d2877eec2f63b931bd47417a81a538327af927da3e |
|||
{{color|green|SHA512/224("")}} |
|||
0x 6ed0dd02806fa89e25de060c19d3ac86cabb87d6a0ddd05c333b84f4 |
|||
{{color|green|SHA512/256("")}} |
|||
0x c672b8d1ef56ed28ab87c3622c5114069bdd3ad7b8f9737498d0c01ecef0967a |
|||
Even a small change in the message will (with overwhelming probability) result in a mostly different hash, due to the [[wikipedia:Avalanche_effect|avalanche effect]]. For example, adding a period to the end of this sentence changes almost half (111 out of 224) of the bits in the hash: |
|||
{{color|green|SHA224("[[The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog]]")}} |
|||
0x 730e109bd7a8a32b1cb9d9a09aa2325d2430587ddbc0c38bad911525 |
|||
{{color|green|SHA224("[[The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog]]{{highlight|.|lightblue}}")}} |
|||
0x 619cba8e8e05826e9b8c519c0a5c68f4fb653e8a3d8aa04bb2c8cd4c |
|||
== Sözde Kodu == |
|||
SHA-256 algoritması için sözde kod aşağıdaki gibidir. W [16..63] kelimelerinin bitleri arasındaki karıştırma işlemlerinin SHA-1'e kıyasla büyük oranda artmıştır. |
|||
{{color|green|''Note 1: All variables are 32 bit unsigned integers and addition is calculated modulo 2<sup>32</sup>''}} |
|||
{{color|green|''Note 2: For each round, there is one round constant k[i] and one entry in the message schedule array w[i], 0 ≤ i ≤ 63''}} |
|||
{{color|green|''Note 3: The compression function uses 8 working variables, a through h}} |
|||
{{color|green|''Note 4: Big-endian convention is used when expressing the constants in this pseudocode,''}} |
|||
{{color|green|''and when parsing message block data from bytes to words, for example,''}} |
|||
{{color|green|''the first word of the input message "abc" after padding is 0x61626380''}} |
|||
{{color|green|''Initialize hash values:''}} |
|||
{{color|green|(first 32 bits of the ''fractional parts'' of the square roots of the first 8 primes 2..19):}} |
|||
h0 := 0x6a09e667 |
|||
h1 := 0xbb67ae85 |
|||
h2 := 0x3c6ef372 |
|||
h3 := 0xa54ff53a |
|||
h4 := 0x510e527f |
|||
h5 := 0x9b05688c |
|||
h6 := 0x1f83d9ab |
|||
h7 := 0x5be0cd19 |
|||
{{color|green|''Initialize array of round constants:''}} |
|||
{{color|green|(first 32 bits of the ''fractional parts'' of the cube roots of the first 64 primes 2..311):}} |
|||
k[0..63] := |
|||
0x428a2f98, 0x71374491, 0xb5c0fbcf, 0xe9b5dba5, 0x3956c25b, 0x59f111f1, 0x923f82a4, 0xab1c5ed5, |
|||
0xd807aa98, 0x12835b01, 0x243185be, 0x550c7dc3, 0x72be5d74, 0x80deb1fe, 0x9bdc06a7, 0xc19bf174, |
|||
0xe49b69c1, 0xefbe4786, 0x0fc19dc6, 0x240ca1cc, 0x2de92c6f, 0x4a7484aa, 0x5cb0a9dc, 0x76f988da, |
|||
0x983e5152, 0xa831c66d, 0xb00327c8, 0xbf597fc7, 0xc6e00bf3, 0xd5a79147, 0x06ca6351, 0x14292967, |
|||
0x27b70a85, 0x2e1b2138, 0x4d2c6dfc, 0x53380d13, 0x650a7354, 0x766a0abb, 0x81c2c92e, 0x92722c85, |
|||
0xa2bfe8a1, 0xa81a664b, 0xc24b8b70, 0xc76c51a3, 0xd192e819, 0xd6990624, 0xf40e3585, 0x106aa070, |
|||
0x19a4c116, 0x1e376c08, 0x2748774c, 0x34b0bcb5, 0x391c0cb3, 0x4ed8aa4a, 0x5b9cca4f, 0x682e6ff3, |
|||
0x748f82ee, 0x78a5636f, 0x84c87814, 0x8cc70208, 0x90befffa, 0xa4506ceb, 0xbef9a3f7, 0xc67178f2 |
|||
{{color|green|''Pre-processing:''}} |
|||
begin with the original message of length L bits |
|||
append a single '1' bit |
|||
append K '0' bits, where K is the minimum number >= 0 such that L + 1 + K + 64 is a multiple of 512 |
|||
append L as a 64-bit big-endian integer, making the total post-processed length a multiple of 512 bits |
|||
{{color|green|''Process the message in successive 512-bit chunks:''}} |
|||
break message into 512-bit chunks |
|||
'''for''' each chunk |
|||
create a 64-entry message schedule array w[0..63] of 32-bit words |
|||
{{color|green|''(The initial values in w[0..63] don't matter, so many implementations zero them here)''}} |
|||
copy chunk into first 16 words w[0..15] of the message schedule array |
|||
{{color|green|''Extend the first 16 words into the remaining 48 words w[16..63] of the message schedule array:''}} |
|||
'''for''' i '''from''' 16 to 63 |
|||
s0 := (w[i-15] '''rightrotate''' 7) '''xor''' (w[i-15] '''rightrotate''' 18) '''xor''' (w[i-15] '''rightshift''' 3) |
|||
s1 := (w[i-2] '''rightrotate''' 17) '''xor''' (w[i-2] '''rightrotate''' 19) '''xor''' (w[i-2] '''rightshift''' 10) |
|||
w[i] := w[i-16] '''+''' s0 '''+''' w[i-7] '''+''' s1 |
|||
{{color|green|''Initialize working variables to current hash value:''}} |
|||
a := h0 |
|||
b := h1 |
|||
c := h2 |
|||
d := h3 |
|||
e := h4 |
|||
f := h5 |
|||
g := h6 |
|||
h := h7 |
|||
{{color|green|''Compression function main loop:''}} |
|||
'''for''' i '''from''' 0 to 63 |
|||
S1 := (e '''rightrotate''' 6) '''xor''' (e '''rightrotate''' 11) '''xor''' (e '''rightrotate''' 25) |
|||
ch := (e '''and''' f) '''xor''' (('''not''' e) '''and''' g) |
|||
temp1 := h '''+''' S1 '''+''' ch '''+''' k[i] '''+''' w[i] |
|||
S0 := (a '''rightrotate''' 2) '''xor''' (a '''rightrotate''' 13) '''xor''' (a '''rightrotate''' 22) |
|||
maj := (a '''and''' b) '''xor''' (a '''and''' c) '''xor''' (b '''and''' c) |
|||
temp2 := S0 '''+''' maj |
|||
h := g |
|||
g := f |
|||
f := e |
|||
e := d '''+''' temp1 |
|||
d := c |
|||
c := b |
|||
b := a |
|||
{{not a typo|a}} := temp1 '''+''' temp2 |
|||
{{color|green|''Add the compressed chunk to the current hash value:''}} |
|||
h0 := h0 '''+''' a |
|||
h1 := h1 '''+''' b |
|||
h2 := h2 '''+''' c |
|||
h3 := h3 '''+''' d |
|||
h4 := h4 '''+''' e |
|||
h5 := h5 '''+''' f |
|||
h6 := h6 '''+''' g |
|||
h7 := h7 '''+''' h |
|||
{{color|green|''Produce the final hash value (big-endian):''}} |
|||
digest := hash := h0 '''append''' h1 '''append''' h2 '''append''' h3 '''append''' h4 '''append''' h5 '''append''' h6 '''append''' h7 |
|||
<code>ch</code> ve <code>maj</code> değerlerinin hesaplanması [[wikipedia:SHA-1#SHA-1_pseudocode|SHA-1]] için anlatıldığı şekilde optimize edilebilir. |
|||
SHA-224 ile SHA-256 aşağıdaki maddeler haricinde aynıdır: |
|||
* İlk özet değeri <code>h0</code> ,<code>h7</code> 'den farlıdır |
|||
* Çıktı <code>h7</code> atlanarak oluşturulmuştur. |
|||
{{color|green|SHA-224 initial hash values (in big endian):}} |
|||
{{color|green|(The second 32 bits of the fractional parts of the square roots of the 9th through 16th primes 23..53)}} |
|||
h[0..7] := |
|||
0xc1059ed8, 0x367cd507, 0x3070dd17, 0xf70e5939, 0xffc00b31, 0x68581511, 0x64f98fa7, 0xbefa4fa4 |
|||
SHA-512 ile SHA-256 aşağıdaki maddeler haricinde yapı olarak aynıdır: |
|||
* Mesaj 1024-bitlik parçalara bölünmüştür, |
|||
* Başlangış değerleri ve tur sabitleri 64 bite uzatılır, |
|||
* 64 yerine 80 tur vardır, |
|||
* Mesaj planlama dizisi w, 64 32-bit kelime yerine 80 64-bit kelime içerir, |
|||
* Mesaj planlama dizisi w'yi genişletmek için, döngü 16 ile 63 aralığında değil 16 ile 79 aralığında çalışır, |
|||
* Tur sabitleri ilk 80 asal sayıdır 2..409, |
|||
* Hesaplamalar için kullanılan kelime boyutu 64 bit uzunluğundadır, |
|||
* the appended length of the message (before pre-processing), in ''bits'', is a 128-bit big-endian integer, and |
|||
* the shift and rotate amounts used are different. |
|||
{{color|green|SHA-512 initial hash values (in big-endian):}} |
|||
{{color|green|}} |
|||
h[0..7] := 0x6a09e667f3bcc908, 0xbb67ae8584caa73b, 0x3c6ef372fe94f82b, 0xa54ff53a5f1d36f1, |
|||
0x510e527fade682d1, 0x9b05688c2b3e6c1f, 0x1f83d9abfb41bd6b, 0x5be0cd19137e2179 |
|||
{{color|green|SHA-512 round constants:}} |
|||
{{color|green|}} |
|||
k[0..79] := [ 0x428a2f98d728ae22, 0x7137449123ef65cd, 0xb5c0fbcfec4d3b2f, 0xe9b5dba58189dbbc, 0x3956c25bf348b538, |
|||
0x59f111f1b605d019, 0x923f82a4af194f9b, 0xab1c5ed5da6d8118, 0xd807aa98a3030242, 0x12835b0145706fbe, |
|||
0x243185be4ee4b28c, 0x550c7dc3d5ffb4e2, 0x72be5d74f27b896f, 0x80deb1fe3b1696b1, 0x9bdc06a725c71235, |
|||
0xc19bf174cf692694, 0xe49b69c19ef14ad2, 0xefbe4786384f25e3, 0x0fc19dc68b8cd5b5, 0x240ca1cc77ac9c65, |
|||
0x2de92c6f592b0275, 0x4a7484aa6ea6e483, 0x5cb0a9dcbd41fbd4, 0x76f988da831153b5, 0x983e5152ee66dfab, |
|||
0xa831c66d2db43210, 0xb00327c898fb213f, 0xbf597fc7beef0ee4, 0xc6e00bf33da88fc2, 0xd5a79147930aa725, |
|||
0x06ca6351e003826f, 0x142929670a0e6e70, 0x27b70a8546d22ffc, 0x2e1b21385c26c926, 0x4d2c6dfc5ac42aed, |
|||
0x53380d139d95b3df, 0x650a73548baf63de, 0x766a0abb3c77b2a8, 0x81c2c92e47edaee6, 0x92722c851482353b, |
|||
0xa2bfe8a14cf10364, 0xa81a664bbc423001, 0xc24b8b70d0f89791, 0xc76c51a30654be30, 0xd192e819d6ef5218, |
|||
0xd69906245565a910, 0xf40e35855771202a, 0x106aa07032bbd1b8, 0x19a4c116b8d2d0c8, 0x1e376c085141ab53, |
|||
0x2748774cdf8eeb99, 0x34b0bcb5e19b48a8, 0x391c0cb3c5c95a63, 0x4ed8aa4ae3418acb, 0x5b9cca4f7763e373, |
|||
0x682e6ff3d6b2b8a3, 0x748f82ee5defb2fc, 0x78a5636f43172f60, 0x84c87814a1f0ab72, 0x8cc702081a6439ec, |
|||
0x90befffa23631e28, 0xa4506cebde82bde9, 0xbef9a3f7b2c67915, 0xc67178f2e372532b, 0xca273eceea26619c, |
|||
0xd186b8c721c0c207, 0xeada7dd6cde0eb1e, 0xf57d4f7fee6ed178, 0x06f067aa72176fba, 0x0a637dc5a2c898a6, |
|||
0x113f9804bef90dae, 0x1b710b35131c471b, 0x28db77f523047d84, 0x32caab7b40c72493, 0x3c9ebe0a15c9bebc, |
|||
0x431d67c49c100d4c, 0x4cc5d4becb3e42b6, 0x597f299cfc657e2a, 0x5fcb6fab3ad6faec, 0x6c44198c4a475817] |
|||
{{color|green|SHA-512 Sum & Sigma:}} |
|||
{{color|green|}} |
|||
S0 := (a '''rightrotate''' 28) '''xor''' (a '''rightrotate''' 34) '''xor''' (a '''rightrotate''' 39) |
|||
S1 := (e '''rightrotate''' 14) '''xor''' (e '''rightrotate''' 18) '''xor''' (e '''rightrotate''' 41) |
|||
{{color|green|}} |
|||
s0 := (w[i-15] '''rightrotate''' 1) '''xor''' (w[i-15] '''rightrotate''' 8) '''xor''' (w[i-15] '''rightshift''' 7) |
|||
s1 := (w[i-2] '''rightrotate''' 19) '''xor''' (w[i-2] '''rightrotate''' 61) '''xor''' (w[i-2] '''rightshift''' 6) |
|||
SHA-384 is identical to SHA-512, except that: |
|||
* the initial hash values <code>h0</code> through <code>h7</code> are different (taken from the 9th through 16th primes), and |
|||
* the output is constructed by omitting <code>h6</code> and <code>h7</code>. |
|||
{{color|green|SHA-384 initial hash values (in big-endian):}} |
|||
{{color|green|}} |
|||
h[0..7] := 0xcbbb9d5dc1059ed8, 0x629a292a367cd507, 0x9159015a3070dd17, 0x152fecd8f70e5939, |
|||
0x67332667ffc00b31, 0x8eb44a8768581511, 0xdb0c2e0d64f98fa7, 0x47b5481dbefa4fa4 |
|||
SHA-512/t is identical to SHA-512 except that: |
|||
* the initial hash values <code>h0</code> through <code>h7</code> are given by the ''SHA-512/t IV generation function'', |
|||
* the output is constructed by truncating the concatenation of <code>h0</code> through <code>h7</code> at ''t'' bits, |
|||
* ''t'' equal to 384 is not allowed, instead SHA-384 should be used as specified, and |
|||
* ''t'' values 224 and 256 are especially mentioned as approved. |
|||
The ''SHA-512/t IV generation function'' evaluates a ''modified SHA-512'' on the ASCII string "SHA-512/''t''", substituted with the decimal representation of ''t''. The ''modified SHA-512'' is the same as SHA-512 except its initial values <code>h0</code> through <code>h7</code> have each been [[wikipedia:XORed|XORed]] with the hexadecimal constant <code>0xa5a5a5a5a5a5a5a5</code>. |
|||
Sample C implementation for SHA-2 family of hash functions can be found in RFC 6234. |
|||
==SHA Fonksiyonlarının Karşılaştırılması== |
|||
Aşağıdaki tabloda, ''iç durum ;'' her bir veri bloğunun sıkıştırma işlemi sonundaki "iç özet değeri toplamı" dır.<blockquote>Daha fazla bilgi için: [[Merkle–Damgård yapısı|Merkle–Damgård construction]]</blockquote> |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin-top: 0px; width:100%" |
|||
|+ SHA Fonksiyonlarının Karşılaştırılması {{Navbar|SHA Fonksiyonlarının Karşılaştırılması|plain=1|style=float:right}} |
|||
|- style="vertical-align:bottom;" |
|||
! colspan="2" | Algoritma ve çeşitleri |
|||
! Çıktı boyutu<br />(bitler) |
|||
! İç durum boyutu<br />(bitler) |
|||
! Blok boyutu<br />(bitler) |
|||
! Maksimum mesaj boyutu<br />(bitler) |
|||
! Turlar |
|||
! İşlemler |
|||
! Güvenlik bitleri<br />(Bilgi) |
|||
! Örnek performans{{refn|Found on an [[AMD Opteron]] 8354 2.2 GHz processor running 64-bit Linux<ref>{{cite web |
|||
| url=http://www.cryptopp.com/benchmarks-amd64.html |
|||
| title=Crypto++ 5.6.0 Benchmarks |
|||
| accessdate=2013-06-13 }} |
|||
</ref>}}<br />([[Mebibyte|MiB]]/s) |
|||
! İlk kez yayınlanışı |
|||
|- style="text-align:center;vertical-align:top;" |
|||
| colspan="2" | '''[[MD5]]''' (referans olarak) || 128 || 128<br>{{nowrap|(4 × 32)}} || 512 || Limitsiz<ref>{{cite web|url=http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc1321 |title=The MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm |date= |accessdate=2016-04-18}}</ref> || 64 || And, Xor, Rot, {{nowrap|Add (mod 2<sup>32</sup>),}} Or || <64 <br /> (çakışma bulundu) || 335 || 1992 |
|||
|- style="text-align:center;vertical-align:top;" |
|||
| colspan="2" | '''{{nowrap|[[SHA-0]]}}''' || 160 || 160<br>{{nowrap|(5 × 32)}} || 512 || 2<sup>64</sup> − 1|| 80 || rowspan="2" | And, Xor, Rot, {{nowrap|Add (mod 2<sup>32</sup>),}} Or || <80 <br /> (çakışma bulundu) || - || 1993 |
|||
|- style="text-align:center;vertical-align:top;" |
|||
| colspan="2" | '''{{nowrap|[[SHA-1]]}}''' || 160 || 160<br>{{nowrap|(5 × 32)}} || 512 || 2<sup>64</sup> − 1 || 80 || <63<br />(çakışma bulundu)<ref>{{cite web|url=https://security.googleblog.com/2017/02/announcing-first-sha1-collision.html |title=Announcing the first SHA1 collision |date= |accessdate=2017-02-23}}</ref> || 192 || 1995 |
|||
|- style="text-align:center;vertical-align:top;" |
|||
| rowspan="2" | '''{{nowrap|[[SHA-2]]}}''' || ''SHA-224''<br />''SHA-256'' || 224<br />256 || 256<br />{{nowrap|(8 × 32)}} || 512 || 2<sup>64</sup> − 1 || 64 || And, Xor, Rot, {{nowrap|Add (mod 2<sup>32</sup>),}} Or, Shr || 112 <br /> || 139 || 2001 |
|||
|- style="text-align:center;vertical-align:top;" |
|||
| ''SHA-384''<br />''SHA-512''<br />''{{nowrap|SHA-512/224}}''<br />''{{nowrap|SHA-512/256}}'' || 384<br />512<br />224 <br />256 || 512<br />{{nowrap|(8 × 64)}} || 1024 || 2<sup>128</sup> − 1 || 80 || And, Xor, Rot, {{nowrap|Add (mod 2<sup>64</sup>),}} Or, Shr || 192<br />256<br />112<br />128 || 154 || 2001 |
|||
|- style="text-align:center;vertical-align:top;" |
|||
| rowspan="2" | '''{{nowrap|[[SHA-3]]}}''' || ''SHA3-224''<br />''SHA3-256''<br />''SHA3-384''<br />''SHA3-512'' || 224<br />256<br />384<br />512 || rowspan="2" | 1600<br>{{nowrap|(5 × 5 × 64)}} || 1152<br />1088<br />832<br />576 || rowspan="2" | Limitsiz<ref>{{cite web|url=http://sponge.noekeon.org/ |title=The Sponge Functions Corner |date= |accessdate=2016-01-27}}</ref>|| rowspan="2" | 24<ref>{{cite web|url=http://keccak.noekeon.org/specs_summary.html |title=The Keccak sponge function family |date= |accessdate=2016-01-27}}</ref> || rowspan="2" | And, Xor, Rot, Not || 112<br />128<br />192<br />256 || - || 2015 |
|||
|- style="text-align:center;vertical-align:top;" |
|||
| ''SHAKE128''<br />''SHAKE256'' || {{nowrap|''d'' (isteğe bağlı)}}<br />{{nowrap|''d'' (isteğe bağlı)}} || 1344<br />1088 || min(''d''/2, 128)<br />min(''d''/2, 256) || - || 2015 |
|||
|} |
|||
İşlemler sütununda, "Rot" [[rotate no carry]] , "Shr" ise [[right logical shift]] işlemlerini ifade eder.SHA-3 dışındakialgoritmaların hepsi, modüler toplama kullanır.<noinclude> |
|||
</noinclude> |
|||
== Kaynakça == |
|||
[[Kategori:Ulusal Güvenlik Teşkilatı]] |
[[Kategori:Ulusal Güvenlik Teşkilatı]] |
||
[[Kategori:Kriptografik algoritmalar]] |
[[Kategori:Kriptografik algoritmalar]] |
||
Sayfanın 21.36, 29 Nisan 2017 tarihindeki hâli
SHA-2, Amerika Birleşik Devletleri Ulusal Güvenlik Ajansı tarafından dizayn edilmiş kriptografik Hash fonksiyonları kümesidir. [1] Kriptografik Hash fonksiyonları, hesaplanmış “hash” (çalıştırılan algoritmanın çıktısı) ile bilinen ve beklenen hash değerinin karşılaştırılmasıyla, dijital veri üzerinde yürüyen matematiksel operasyonlardır. Herhangi bir kişi verinin bütünlüğüne karar verebilir. Örneğin, yüklenmiş bir dosyanın hash ’ini hesaplamak ve sonucu önceden açıklanmış hash sonucu ile karşılaştırmak, yüklemenin değiştirilip değiştirilmediğini veya üzerinde oynama yapılıp yapılmadığını gösterebilir. [2] Kriptografik Hash fonksiyonlarının kilit noktası çakışma dirençleridir: hiç kimse aynı hash çıktısı veren iki farklı girdi bulamamalı.
SHA-2, kendinden önce gelen SHA-1’den önemli farklılıklar içermektedir. SHA-2 ailesi basamakları (hash değerleri) 224, 256, 384 veya 512 bit olan altı hash fonksiyonundan oluşur: SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512, SHA-512/224, SHA-512/256.SHA-256 ve SHA-512 sırasıyla 32-bit ve 64-bitlik kelimelerle hesaplanmış orijinal hash fonksiyonlarıdır. Farklı kaydırma miktarları ve toplama sabitleri kullanırlar ancak yapıları neredeyse aynıdır sadece yuvarlama sayısında farklıdırlar. SHA-224 ve SHA-384 ilk ikisinin farklı başlangıç değerleri ile hesaplanmış, basitçe kesilmiş versiyonlarıdır. SHA-512/224 ve SHA-512/256 da SHA-512’nin kesilmiş versiyonlarıdır ama başlangıç değerleri Federal Bilgi İşleme Standardı (FIPS) PUB 180-4’te tanımlanmış metot kullanılarak üretilmiştir. SHA-2, Ulusal Standartlar ve Teknoloji Enstitüsü (NIST) bir Birleşik Devletler federal standardı (FIPS) tarafından 2001’de yayınlanmıştır. SHA-2 algoritmalar ailesi Birleşik Devletler 6829355 patentinde patentlenmiştir.[3] Birleşik Devletler patenti telifsiz lisans altında yayımlamıştır.[4]
2005’te, SHA-1 çakışmalarını önceden mümkün olduğu düşünülenden 2000 daha az adımda bulmak için bir algoritma geliştirilmiştir. [5] 2017’de SHA-1 çakışmasının bir örneği yayımlanmıştır.[6] SHA-1 tarafından bırakılan güvenlik marjini planlanandan zayıftır ve bu sebeple, kullanımı artık dijital imzalar gibi çakışma direncine bağımlı uygulamalar için önerilmemektedir. SHA-2, SHA-1 algoritmasına bazı benzerlikler taşısa da, bu ataklar SHA-2’ye başarılı bir şekilde genişletilememiştir.
Şu anda en iyi açık ataklar, aşağıda Kriptanaliz ve Doğrulama bölümünde gösterildiği gibi SHA-256’nın 52 yuvarlaması veya SHA-512’nin 57 yuvarlaması için öngörüntü direncini ve SHA-256’nin 46 yuvarlaması için çakışma direncini kırmaktadır. [7][8]
Hash Standartları
FIPS PUB 180-2’nin yayımlanmasıyla, NIST SHA ailesinde üç tane ek hash fonksiyonu eklemiştir. Algoritmalar toplu olarak SHA-2 diye bilinir ve basamak uzunlukları (bit cinsinden) ile isimlendirilmişlerdir: SHA-256, SHA-384, ve SHA-512.
Algoritmalar ilk olarak 2001’de FIPS PUB 180-2 taslağında, public review and comments (kamu değerlendirmesi ve yorumları???) kabul edildiğinde, yayımlanmışlardır. Ağustos 2002’de FIPS PUB 180-2, Nisan 1995’te yayımlanan FIPS PUB 180-1’in yerini alarak yeni Güvenli Hash Standardı haline geldi. Güncellenmiş standart, SHA-2 ailesinin iç çalışmalarını tanımlamasıyla tutarlı güncellenmiş teknik notasyonla birlikte orijinal SHA-1 algoritmasını içerir. [9]
Şubat 2004’te FIPS PUB 180-2 için, iki anahtarlı Üçlü DES’in anahtar uzunluğuyla eşleşmesi amacıyla tanımlanmış ek bir değişkeni,SHA-224, belirten bir değişiklik bildirimi yayımlandı. [10] Ekim 2008’de standart, FIPS PUB 180-3’te değişiklik bildirimindeki SHA-224 dahil güncellendi, ama bunun dışında standartta başka temel değişim yapılmadı. Standardı güncellemekteki başlıca motivasyon hash algoritmaları ve kullanım önerileri hakkındaki güvenlik bilgisini Special Publications 800-107 ve 800-57’ye yeniden yerleştirmekti.[11] [12][13]Detaylı test verisi ve örnek mesaj özetleri de standarttan kaldırıldı ve ayrı belge olarak temin edildi.[14]
In January 2011, NIST published SP800-131A, which specified a move from the current minimum security of 80-bits (provided by SHA-1) allowable for federal government use until the end of 2013, with 112-bit security (provided by SHA-2) being the minimum requirement current thereafter, and the recommended security level from the publication date. [15]
Mart 2012’de standart, SHA-512/224 ve SHA-512/256 hash fonksiyonları eklenerek ve SHA-512’nin kesilmiş versiyonları için başlangıç değerleri üretmek üzere bir metot tanımlanarak FIPS PUB 180-4’te güncellendi. Buna ek olarak, gerçek-zamanlı video veya ses beslemesi gibi hash verisinin içerik üretimi ile aynı anda hesaplanmasına izin verilerek, girdi verisini hash hesaplamasından önce eklemedeki kısıtlama kaldırıldı. Son veri bloğunu eklemek hala hash çıktısından önce gerçekleştirilmelidir. [16]
Temmuz 2012’de NIST, kriptografik anahtar yönetimi için rehberlik sağlayan SP800-57’yi tekrar gözden geçirdi. Yayın, 2013’ten sonra hash güvenliği 112-bitten az olan dijital imzaların üretilmesine izin vermemektedir. 2007’de olan önceki gözden geçirme kesmenin 2010’un sonu olacağını belirtmişti??????.[13] Ağustos 2012’de NIST, SP800-107’yi aynı şekilse gözden geçirdi.[12]
NIST hash fonksiyonu yarışması yeni hash fonksiyonu SHA-3’ü 2012 yılında seçti.[17] SHA-3 algoritması, SHA-2’den türetilmemiştir.
Uygulamalar
Kriptanaliz ve Doğrulama
Resmi Doğrulama
Test Değerleri
Hash values of an empty string (i.e., a zero-length input text).
SHA224("") 0x d14a028c2a3a2bc9476102bb288234c415a2b01f828ea62ac5b3e42f SHA256("") 0x e3b0c44298fc1c149afbf4c8996fb92427ae41e4649b934ca495991b7852b855 SHA384("") 0x 38b060a751ac96384cd9327eb1b1e36a21fdb71114be07434c0cc7bf63f6e1da274edebfe76f65fbd51ad2f14898b95b SHA512("") 0x cf83e1357eefb8bdf1542850d66d8007d620e4050b5715dc83f4a921d36ce9ce47d0d13c5d85f2b0ff8318d2877eec2f63b931bd47417a81a538327af927da3e SHA512/224("") 0x 6ed0dd02806fa89e25de060c19d3ac86cabb87d6a0ddd05c333b84f4 SHA512/256("") 0x c672b8d1ef56ed28ab87c3622c5114069bdd3ad7b8f9737498d0c01ecef0967a
Even a small change in the message will (with overwhelming probability) result in a mostly different hash, due to the avalanche effect. For example, adding a period to the end of this sentence changes almost half (111 out of 224) of the bits in the hash:
SHA224("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog") 0x 730e109bd7a8a32b1cb9d9a09aa2325d2430587ddbc0c38bad911525 SHA224("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.") 0x 619cba8e8e05826e9b8c519c0a5c68f4fb653e8a3d8aa04bb2c8cd4c
Sözde Kodu
SHA-256 algoritması için sözde kod aşağıdaki gibidir. W [16..63] kelimelerinin bitleri arasındaki karıştırma işlemlerinin SHA-1'e kıyasla büyük oranda artmıştır.
Note 1: All variables are 32 bit unsigned integers and addition is calculated modulo 232 Note 2: For each round, there is one round constant k[i] and one entry in the message schedule array w[i], 0 ≤ i ≤ 63 Note 3: The compression function uses 8 working variables, a through h Note 4: Big-endian convention is used when expressing the constants in this pseudocode, and when parsing message block data from bytes to words, for example, the first word of the input message "abc" after padding is 0x61626380 Initialize hash values: (first 32 bits of the fractional parts of the square roots of the first 8 primes 2..19): h0 := 0x6a09e667 h1 := 0xbb67ae85 h2 := 0x3c6ef372 h3 := 0xa54ff53a h4 := 0x510e527f h5 := 0x9b05688c h6 := 0x1f83d9ab h7 := 0x5be0cd19 Initialize array of round constants: (first 32 bits of the fractional parts of the cube roots of the first 64 primes 2..311): k[0..63] := 0x428a2f98, 0x71374491, 0xb5c0fbcf, 0xe9b5dba5, 0x3956c25b, 0x59f111f1, 0x923f82a4, 0xab1c5ed5, 0xd807aa98, 0x12835b01, 0x243185be, 0x550c7dc3, 0x72be5d74, 0x80deb1fe, 0x9bdc06a7, 0xc19bf174, 0xe49b69c1, 0xefbe4786, 0x0fc19dc6, 0x240ca1cc, 0x2de92c6f, 0x4a7484aa, 0x5cb0a9dc, 0x76f988da, 0x983e5152, 0xa831c66d, 0xb00327c8, 0xbf597fc7, 0xc6e00bf3, 0xd5a79147, 0x06ca6351, 0x14292967, 0x27b70a85, 0x2e1b2138, 0x4d2c6dfc, 0x53380d13, 0x650a7354, 0x766a0abb, 0x81c2c92e, 0x92722c85, 0xa2bfe8a1, 0xa81a664b, 0xc24b8b70, 0xc76c51a3, 0xd192e819, 0xd6990624, 0xf40e3585, 0x106aa070, 0x19a4c116, 0x1e376c08, 0x2748774c, 0x34b0bcb5, 0x391c0cb3, 0x4ed8aa4a, 0x5b9cca4f, 0x682e6ff3, 0x748f82ee, 0x78a5636f, 0x84c87814, 0x8cc70208, 0x90befffa, 0xa4506ceb, 0xbef9a3f7, 0xc67178f2 Pre-processing: begin with the original message of length L bits append a single '1' bit append K '0' bits, where K is the minimum number >= 0 such that L + 1 + K + 64 is a multiple of 512 append L as a 64-bit big-endian integer, making the total post-processed length a multiple of 512 bits Process the message in successive 512-bit chunks: break message into 512-bit chunks for each chunk create a 64-entry message schedule array w[0..63] of 32-bit words (The initial values in w[0..63] don't matter, so many implementations zero them here) copy chunk into first 16 words w[0..15] of the message schedule array Extend the first 16 words into the remaining 48 words w[16..63] of the message schedule array: for i from 16 to 63 s0 := (w[i-15] rightrotate 7) xor (w[i-15] rightrotate 18) xor (w[i-15] rightshift 3) s1 := (w[i-2] rightrotate 17) xor (w[i-2] rightrotate 19) xor (w[i-2] rightshift 10) w[i] := w[i-16] + s0 + w[i-7] + s1 Initialize working variables to current hash value: a := h0 b := h1 c := h2 d := h3 e := h4 f := h5 g := h6 h := h7 Compression function main loop: for i from 0 to 63 S1 := (e rightrotate 6) xor (e rightrotate 11) xor (e rightrotate 25) ch := (e and f) xor ((not e) and g) temp1 := h + S1 + ch + k[i] + w[i] S0 := (a rightrotate 2) xor (a rightrotate 13) xor (a rightrotate 22) maj := (a and b) xor (a and c) xor (b and c) temp2 := S0 + maj h := g g := f f := e e := d + temp1 d := c c := b b := a Şablon:Not a typo := temp1 + temp2 Add the compressed chunk to the current hash value: h0 := h0 + a h1 := h1 + b h2 := h2 + c h3 := h3 + d h4 := h4 + e h5 := h5 + f h6 := h6 + g h7 := h7 + h Produce the final hash value (big-endian): digest := hash := h0 append h1 append h2 append h3 append h4 append h5 append h6 append h7
ch ve maj değerlerinin hesaplanması SHA-1 için anlatıldığı şekilde optimize edilebilir.
SHA-224 ile SHA-256 aşağıdaki maddeler haricinde aynıdır:
- İlk özet değeri
h0,h7'den farlıdır - Çıktı
h7atlanarak oluşturulmuştur.
SHA-224 initial hash values (in big endian): (The second 32 bits of the fractional parts of the square roots of the 9th through 16th primes 23..53) h[0..7] := 0xc1059ed8, 0x367cd507, 0x3070dd17, 0xf70e5939, 0xffc00b31, 0x68581511, 0x64f98fa7, 0xbefa4fa4
SHA-512 ile SHA-256 aşağıdaki maddeler haricinde yapı olarak aynıdır:
- Mesaj 1024-bitlik parçalara bölünmüştür,
- Başlangış değerleri ve tur sabitleri 64 bite uzatılır,
- 64 yerine 80 tur vardır,
- Mesaj planlama dizisi w, 64 32-bit kelime yerine 80 64-bit kelime içerir,
- Mesaj planlama dizisi w'yi genişletmek için, döngü 16 ile 63 aralığında değil 16 ile 79 aralığında çalışır,
- Tur sabitleri ilk 80 asal sayıdır 2..409,
- Hesaplamalar için kullanılan kelime boyutu 64 bit uzunluğundadır,
- the appended length of the message (before pre-processing), in bits, is a 128-bit big-endian integer, and
- the shift and rotate amounts used are different.
SHA-512 initial hash values (in big-endian): h[0..7] := 0x6a09e667f3bcc908, 0xbb67ae8584caa73b, 0x3c6ef372fe94f82b, 0xa54ff53a5f1d36f1, 0x510e527fade682d1, 0x9b05688c2b3e6c1f, 0x1f83d9abfb41bd6b, 0x5be0cd19137e2179 SHA-512 round constants: k[0..79] := [ 0x428a2f98d728ae22, 0x7137449123ef65cd, 0xb5c0fbcfec4d3b2f, 0xe9b5dba58189dbbc, 0x3956c25bf348b538, 0x59f111f1b605d019, 0x923f82a4af194f9b, 0xab1c5ed5da6d8118, 0xd807aa98a3030242, 0x12835b0145706fbe, 0x243185be4ee4b28c, 0x550c7dc3d5ffb4e2, 0x72be5d74f27b896f, 0x80deb1fe3b1696b1, 0x9bdc06a725c71235, 0xc19bf174cf692694, 0xe49b69c19ef14ad2, 0xefbe4786384f25e3, 0x0fc19dc68b8cd5b5, 0x240ca1cc77ac9c65, 0x2de92c6f592b0275, 0x4a7484aa6ea6e483, 0x5cb0a9dcbd41fbd4, 0x76f988da831153b5, 0x983e5152ee66dfab, 0xa831c66d2db43210, 0xb00327c898fb213f, 0xbf597fc7beef0ee4, 0xc6e00bf33da88fc2, 0xd5a79147930aa725, 0x06ca6351e003826f, 0x142929670a0e6e70, 0x27b70a8546d22ffc, 0x2e1b21385c26c926, 0x4d2c6dfc5ac42aed, 0x53380d139d95b3df, 0x650a73548baf63de, 0x766a0abb3c77b2a8, 0x81c2c92e47edaee6, 0x92722c851482353b, 0xa2bfe8a14cf10364, 0xa81a664bbc423001, 0xc24b8b70d0f89791, 0xc76c51a30654be30, 0xd192e819d6ef5218, 0xd69906245565a910, 0xf40e35855771202a, 0x106aa07032bbd1b8, 0x19a4c116b8d2d0c8, 0x1e376c085141ab53, 0x2748774cdf8eeb99, 0x34b0bcb5e19b48a8, 0x391c0cb3c5c95a63, 0x4ed8aa4ae3418acb, 0x5b9cca4f7763e373, 0x682e6ff3d6b2b8a3, 0x748f82ee5defb2fc, 0x78a5636f43172f60, 0x84c87814a1f0ab72, 0x8cc702081a6439ec, 0x90befffa23631e28, 0xa4506cebde82bde9, 0xbef9a3f7b2c67915, 0xc67178f2e372532b, 0xca273eceea26619c, 0xd186b8c721c0c207, 0xeada7dd6cde0eb1e, 0xf57d4f7fee6ed178, 0x06f067aa72176fba, 0x0a637dc5a2c898a6, 0x113f9804bef90dae, 0x1b710b35131c471b, 0x28db77f523047d84, 0x32caab7b40c72493, 0x3c9ebe0a15c9bebc, 0x431d67c49c100d4c, 0x4cc5d4becb3e42b6, 0x597f299cfc657e2a, 0x5fcb6fab3ad6faec, 0x6c44198c4a475817] SHA-512 Sum & Sigma: S0 := (a rightrotate 28) xor (a rightrotate 34) xor (a rightrotate 39) S1 := (e rightrotate 14) xor (e rightrotate 18) xor (e rightrotate 41) s0 := (w[i-15] rightrotate 1) xor (w[i-15] rightrotate 8) xor (w[i-15] rightshift 7) s1 := (w[i-2] rightrotate 19) xor (w[i-2] rightrotate 61) xor (w[i-2] rightshift 6)
SHA-384 is identical to SHA-512, except that:
- the initial hash values
h0throughh7are different (taken from the 9th through 16th primes), and - the output is constructed by omitting
h6andh7.
SHA-384 initial hash values (in big-endian):
h[0..7] := 0xcbbb9d5dc1059ed8, 0x629a292a367cd507, 0x9159015a3070dd17, 0x152fecd8f70e5939,
0x67332667ffc00b31, 0x8eb44a8768581511, 0xdb0c2e0d64f98fa7, 0x47b5481dbefa4fa4
SHA-512/t is identical to SHA-512 except that:
- the initial hash values
h0throughh7are given by the SHA-512/t IV generation function, - the output is constructed by truncating the concatenation of
h0throughh7at t bits, - t equal to 384 is not allowed, instead SHA-384 should be used as specified, and
- t values 224 and 256 are especially mentioned as approved.
The SHA-512/t IV generation function evaluates a modified SHA-512 on the ASCII string "SHA-512/t", substituted with the decimal representation of t. The modified SHA-512 is the same as SHA-512 except its initial values h0 through h7 have each been XORed with the hexadecimal constant 0xa5a5a5a5a5a5a5a5.
Sample C implementation for SHA-2 family of hash functions can be found in RFC 6234.
SHA Fonksiyonlarının Karşılaştırılması
Aşağıdaki tabloda, iç durum ; her bir veri bloğunun sıkıştırma işlemi sonundaki "iç özet değeri toplamı" dır.
Daha fazla bilgi için: Merkle–Damgård construction
| Algoritma ve çeşitleri | Çıktı boyutu (bitler) |
İç durum boyutu (bitler) |
Blok boyutu (bitler) |
Maksimum mesaj boyutu (bitler) |
Turlar | İşlemler | Güvenlik bitleri (Bilgi) |
Örnek performans[19] (MiB/s) |
İlk kez yayınlanışı | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD5 (referans olarak) | 128 | 128 (4 × 32) |
512 | Limitsiz[20] | 64 | And, Xor, Rot, Add (mod 232), Or | <64 (çakışma bulundu) |
335 | 1992 | |
| SHA-0 | 160 | 160 (5 × 32) |
512 | 264 − 1 | 80 | And, Xor, Rot, Add (mod 232), Or | <80 (çakışma bulundu) |
- | 1993 | |
| SHA-1 | 160 | 160 (5 × 32) |
512 | 264 − 1 | 80 | <63 (çakışma bulundu)[21] |
192 | 1995 | ||
| SHA-2 | SHA-224 SHA-256 |
224 256 |
256 (8 × 32) |
512 | 264 − 1 | 64 | And, Xor, Rot, Add (mod 232), Or, Shr | 112 |
139 | 2001 |
| SHA-384 SHA-512 SHA-512/224 SHA-512/256 |
384 512 224 256 |
512 (8 × 64) |
1024 | 2128 − 1 | 80 | And, Xor, Rot, Add (mod 264), Or, Shr | 192 256 112 128 |
154 | 2001 | |
| SHA-3 | SHA3-224 SHA3-256 SHA3-384 SHA3-512 |
224 256 384 512 |
1600 (5 × 5 × 64) |
1152 1088 832 576 |
Limitsiz[22] | 24[23] | And, Xor, Rot, Not | 112 128 192 256 |
- | 2015 |
| SHAKE128 SHAKE256 |
d (isteğe bağlı) d (isteğe bağlı) |
1344 1088 |
min(d/2, 128) min(d/2, 256) |
- | 2015 | |||||
İşlemler sütununda, "Rot" rotate no carry , "Shr" ise right logical shift işlemlerini ifade eder.SHA-3 dışındakialgoritmaların hepsi, modüler toplama kullanır.
Kaynakça
- ^ "On the Secure Hash Algorithm family" (PDF).
- ^ "Cryptographic Hash Function". About.com
- ^ US 6829355
- ^ "Licensing Declaration for US patent 6829355.".
- ^ "Schneier on Security: Cryptanalysis of SHA-1". Schneier.com.
- ^ Cryptology Group at Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica (CWI) and the Google Research Security, Privacy and Anti-abuse Group. "Shattered: We have broken SHA-1 in practice". SHAttered.
- ^ Dmitry Khovratovich, Christian Rechberger & Alexandra Savelieva (2011). "Bicliques for Preimages: Attacks on Skein-512 and the SHA-2 family" (PDF). IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive. 2011:286.
- ^ Mario Lamberger & Florian Mendel (2011). "Higher-Order Differential Attack on Reduced SHA-256" (PDF). IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive. 2011:37.
- ^ Federal Register Notice 02-21599, Announcing Approval of FIPS Publication 180-2
- ^ "FIPS 180-2 with Change Notice 1" (PDF). csrc.nist.gov
- ^ Federal Register Notice E8-24743, Announcing Approval of FIPS Publication 180-3
- ^ a b FIPS SP 800-107 Recommendation for Applications Using Approved Hash Algorithms
- ^ a b FIPS SP 800-57 Recommendation for Key Management: Part 1: General
- ^ "NIST.gov - Computer Security Division - Computer Security Resource Center"
- ^ FIPS SP 800-131A Recommendation for Transitioning the Use of Cryptographic Algorithms and Key Lengths
- ^ Federal Register Notice 2012-5400, Announcing Approval of FIPS Publication 180-4
- ^ "NIST Selects Winner of Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA-3) Competition"
- ^ "Crypto++ 5.6.0 Benchmarks". Erişim tarihi: 2013-06-13.
- ^ Found on an AMD Opteron 8354 2.2 GHz processor running 64-bit Linux[18]
- ^ "The MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm". Erişim tarihi: 2016-04-18.
- ^ "Announcing the first SHA1 collision". Erişim tarihi: 2017-02-23.
- ^ "The Sponge Functions Corner". Erişim tarihi: 2016-01-27.
- ^ "The Keccak sponge function family". Erişim tarihi: 2016-01-27.





